What damage was caused by the nuclear accident? How did Japan’s electricity and energy supply/demand change after the nuclear accident? Here we use infographics to summarize the key issues.
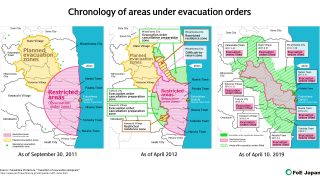
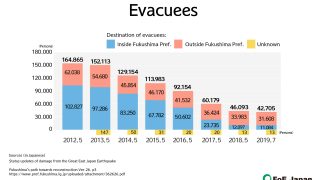
- Thousands of people had to evacuate due to the nuclear accident.
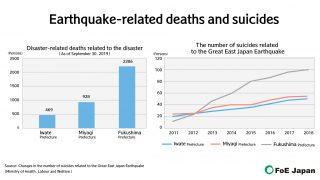
- The earthquake took a heavy toll in deaths and suicides.
- The government has terminated housing support for evacuees, practically forcing them to return home.
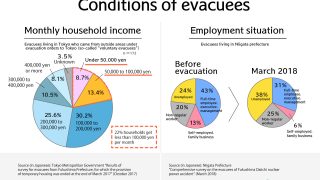
- Evacuees continue to suffer financially nearly a decade later.
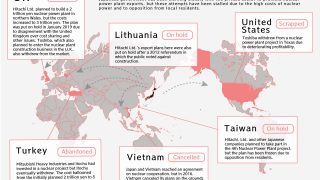
- The Japanese government and industry have been trying to export nuclear power, but failures mount.
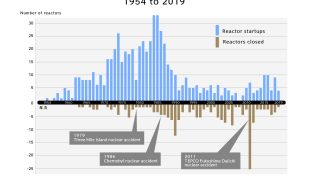
- Nuclear power is declining globally.
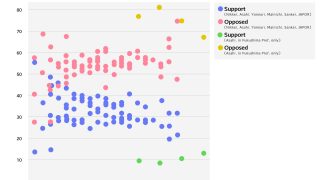
- Public opinion in Japan is strongly against the restart of nuclear plants.
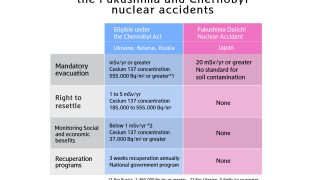
- The Japanese response was more lax in some ways even compared to Chernobyl.
- Many communities are still paying a heavy price for the nuclear accident, with the total return rate of evacuees at only 28% even now.
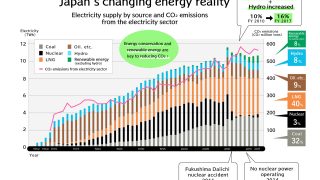
- With energy conservation and renewable energy, Japan could phase out nuclear energy.
- High costs and many safety problems have prevented most nuclear reactors from restarting in Japan.
- Nuclear power, once considered cheap, is now the most expensive source of electricity, while renewables are looking better and better.
- Soil contamination from the nuclear accident was huge, and the problems continue.
- Costs of the nuclear accident are enormous, with the latest estimates as high as 81 trillion yen, which may ultimately have to be paid by the public.
- Solar power and other renewable forms of energy are variable, but there are many effective ways to compensate.
- The government wants to dump radioactive water into the oceans, but fishermen are opposed, and there are better alternatives.